Understanding PSU form factors
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Don't have an account?
Creating an account has many benefits: check out faster, keep more than one address, track orders and more.
Beyond size and shape of the PSU, the form factor also determines the size, shape and placement of connectors, placement of the mounting hole, as well as slots and pinouts which will place limitations on where you can position it in your system
What is the power supply?
Certainly nobody’s first choice when it comes to the coolest component of your custom gaming PC, the power supply unit (PSU) is no less important. Without the PSU, no power is being supplied to your system, and with no power, it doesn’t matter how advanced your graphics card is or how fast your processor is!
While the PSU might seem like a simple power brick, there are a few things you should consider when choosing one.
Firstly, not all PSUs are created equal. If you want power supplied to your system reliably, you should be prepared to invest in a high-quality PSU.
As you shop around for power supplies, you will start to notice that there are a range of wattages available. The simple way to think of wattage is; the higher your wattage, the more power to your system. This seems simple enough, but depending on what components you have in your system, you will have higher or lower power requirements, and you need to make sure you have a PSU with a high enough wattage to power everything.
The simplest way to calculate your PCs power requirements is by using an online PSU calculator. These online tools allow you to list your PCs components and in return, they give you your systems minimum wattage requirement, although we recommend going for slightly higher than the minimum to be safe.
Next, you should consider the connections you need and what connections are available on your chosen PSU. There’s nothing worse than discovering you don’t have the connection points that you need for all your components.
Lastly, before we get into form factors, you should be considering efficiency. The efficiency of your PSU determines how much power is wasted and how much heat is produced – both things that you want to minimise. Thankfully, there is a simple to understand rating system for PSUs that helps you quickly determine efficiency. The “80 Plus” rating system guarantees that a power supply unit is at least 80% efficient (with only 20% of power lost as heat. The rating system includes:
- 80 PLUS
- 80 PLUS Bronze
- 80 PLUS Silver
- 80 PLUS Gold
- 80 PLUS Platinum
- 80 PLUS Titanium
With the efficiency increasing the further up the precious metals you get.
If you're buying Corsair PSUs, it is worth noting that Corsair has recently abandoned the 80 Plus ratings for its power supplies, and is making the move to an efficiency standard from Cybenetics. It's a fairly straightforward transition though, because 80 Plus Gold (for example) is the equivalent of Cybentetics Gold. Cybenetics use Diamond to represent ≥93% overall efficiency, and then use Platinum, Gold, Silver and Bronze, which are equivalent to the 80 Plus ratings.
Corsair has made this move because they feel the Cybenetics rating and testing is more robust, thorough and accurate.
Let's talk PSU form factors
So, what is a form factor and why does it play a part in choosing a PSU?
Form factor refers to the shape, size and layout of a component. It is a fixed set of dimensions that is (mostly) standardised, meaning that, in general, you can substitute a component of one form factor, for a different component of the same form factor.
As the form factor is a pre-determined size and shape for your components, your choice of form factor will determine the size of your final build. If you’re looking to build a small form factor system, choosing large form factor components just isn’t physically going to work.
Beyond size and shape of the PSU, the form factor also determines the size, shape and placement of connectors, placement of the mounting hole, as well as slots and pinouts which will place limitations on where you can position it in your system so its important to pay it due consideration.
What are the form factors?
The form-factors you should be aware of when buying gaming-grade power supplies are;
- ATX
- TFX
- SFX
- SFX-L
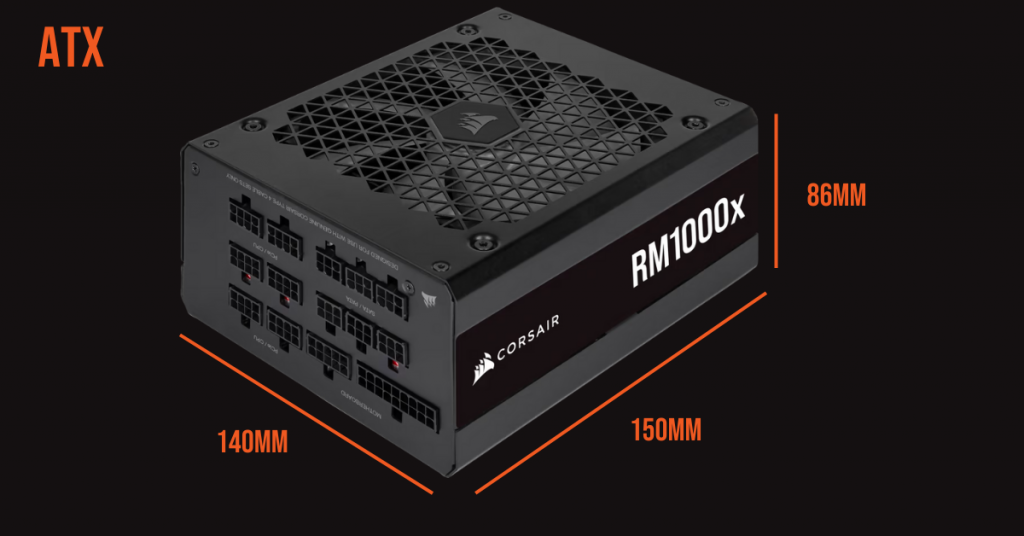
ATX
ATX PS/2 is the most common PSU form factor, because it can be used in most systems, will fit in most PC cases (from Micro-ATX upward) and come in a wide variety of wattage ratings. The standard dimensions of this form factor are 150mm (W) x 86mm (H) x 140mm (D) although you should check your individual manufacturer specifications for these dimensions as the depth can often vary.
ATX form factor PSUs usually have either a 20 or 24-pin main power connector, as well as various SATA and PCIe connectors.
TFX
Not hugely popular for gaming systems, the TFX form factor PSUs are thin, making them a great choice for ultra-slim desktops, none-standard shaped systems or compact media centres. TFX PSUs are generally lower wattage and offer only basic connectivity, so you’ll need to carefully consider your other components if you go for this form factor.
SFX
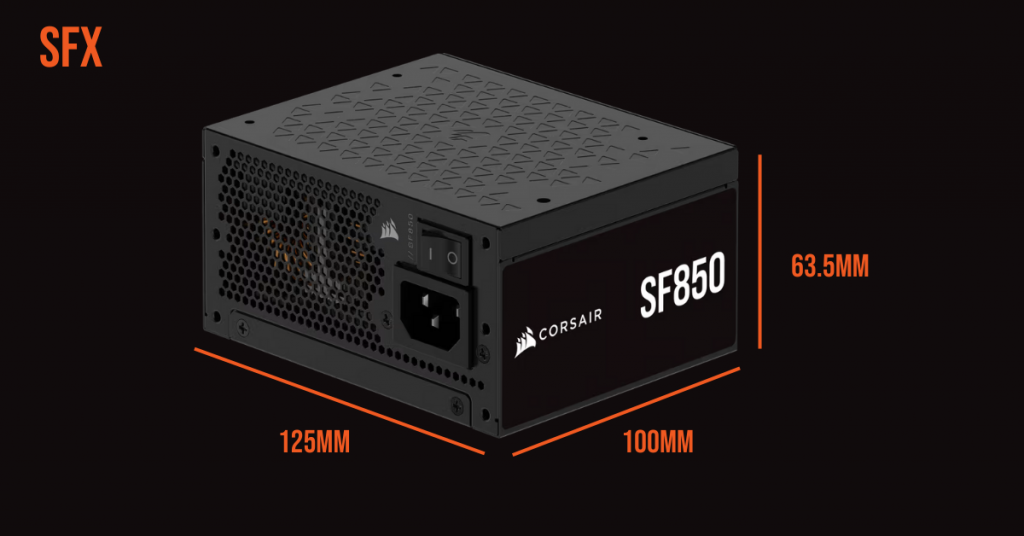
Typically a better option for small gaming systems than the TFX form factor, SFX power supplies offer up to 1300W and can fit in mini-ITX or micro-ATX cases as well as cases that support ATX PS/2 form factor PSUs, though this may require some simple adapters or brackets. The standard dimensions for this form factor are 125mm (W) x 63.5mm (H) x 100mm (D).
SFX form factor PSUs are compact and designed for small form factor PC builds, without compromising on power and connectivity, making them a great choice for high-power, compact builds.

SFX-L
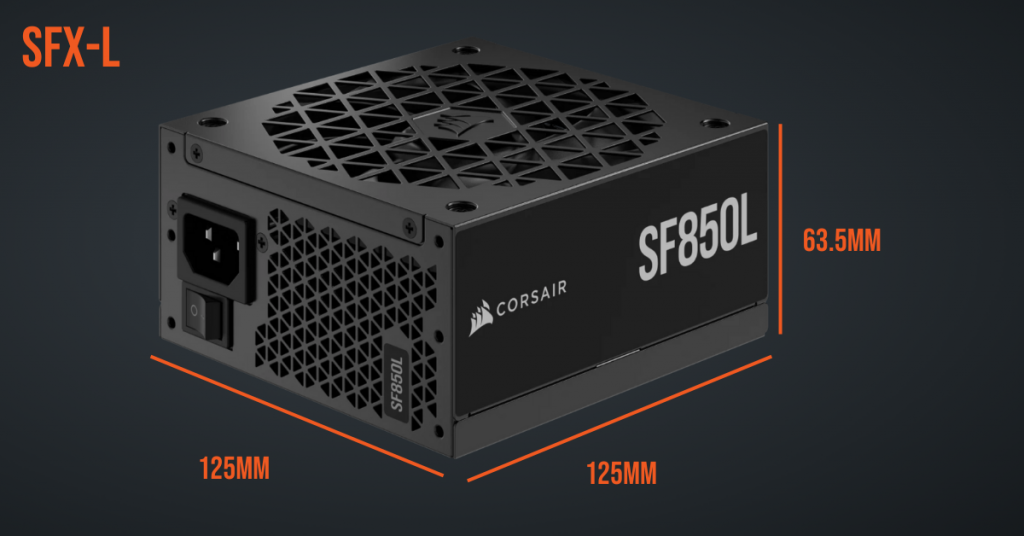
The larger cousin of the SFX PSU form factor, SFX-L PSUs are still designed to be space efficient and fit into smaller cases (like micro-ATX) but their longer form factor gives space for larger fans and better cooling, making them a great option for systems where a smaller footprint is needed, but heat management and dissipation is a priority.
The SFX-L dimensions are typically 125mm x 125mm x 63.5mm, although many people will use the term SFX-L to describe any SFX PSU where the length is more than 100mm.

Connectors and pinouts
If you’re considering your PSU form factor, it is also worth thinking about the connectors and cables that you will need to provide power to your various components. These connectors are:
20 + 4 pin ATX power connector: Used to connect your motherboard to your PSU. Originally this was a 20 pin connector, but as modern day motherboards require more power, an additional 4 pins were added, hence the ’20 + 4’ configuration.
4 +4 pin power connector: Also connecting to the motherboard, the 4 + 4 pin connector is what is powering your CPU.
SATA power connector: These connectors are powering your SATA hard drives, solid state drives, and optical drives.
Molex power connector: Not used much today, the Molex cable connector was used to power older hardware such as fans and occasional accessories like LED strips.
6 + 2 pin PCIe power connector: This connector is used to power your graphics card and, depending on your GPU and its power requirements, you may need more than one.
The form factor of your PSU can affect its compatibility with certain motherboards, due to the connectors available, and older PSUs may have connectors and cables that are now obsolete or can damage your components. If you’re buying a PSU, it is always worth looking to the manufacturer specifications of all your hardware to ensure compatibility, or if you have any questions, you can always contact our expert customer service team on [email protected].
Choosing the appropriate form factor: What to consider when selecting a PSU
We hope this has been a useful introduction to PSU form factors. As you can probably see, there is a fair amount to consider when shopping for your humble power supply unit. Whilst it can seem confusing, the main points to consider are;
Build size:
What size of system do you want? If you are limited by space or where your gaming system can be located, then choosing large form factor components is going to cause issues for you. The form factor of one component will often influence the form factor of another component, and ultimately the size of your final PC build.
Compatibility:
An ATX PSU isn’t going to fit in an ultra-small form factor or mini-ATX case. Similarly, a TFX form factor PSU probably isn’t going to supply the power you need for that RTX 4090 you’re running. It’s important when deciding on PSU form factor that you pay attention to the rating, dimensions and connectors and cables available, so that you don’t run into compatibility issues further down the line.
Power requirements:
An obvious one, but make sure whatever PSU you choose, it can supply enough power to your system. Use an online calculator, check the minimum requirements for your gaming PC, and then choose a PSU that gives you a bit of headroom above that minimum to account for spikes.
A Word on Modular vs. Fixed
One final consideration when it comes to all things PSU form factor is ‘modular’ vs. ‘fixed’. A modular power supply doesn’t come with pre-attached cables, allowing you to choose only the cables you need. This results in a cleaner build, less clutter and potentially more efficient airflow for your system. It’s worth noting with a modular system that you should avoid mixing and matching cable manufacturers and models, because, while the ends which connect to your components are standard ends, the connections to your PSU aren’t necessarily. You don’t want to end up buying cables for a modular unit that aren’t compatible.
A fixed power supply unit, by comparison, has all the cables pre-soldered, including the ones you may not need. This is an important consideration, because you will need to find the space for these cables within your chassis, regardless of whether you use them or not. You will also need to think about cable management and efficiently moving air through your system with the reduced space.
There is also a halfway option, known as a semi-modular which comes with the most commonly used cables pre-attached (typically the 24-pin, 8-pin and PCIe cables). If you need any other connectors, you can add them which gives you more flexibility than the fixed module.
There is no right or wrong with this, it really comes down to personal preference and your own requirements, but it is worth talking about when considering form factor as the cable arrangement will have a knock-on effect on space.
So there you have it – PSU form factors explained and what it means when you’re building or upgrading your system. As you can see, the power supply should never be a last-minute consideration. If you want to take any doubts out of the equation, why not take a look at our huge range of preconfigured and configurable gaming PCs? Or, if you like to build systems yourself, check out our components store for a range of power supply units.